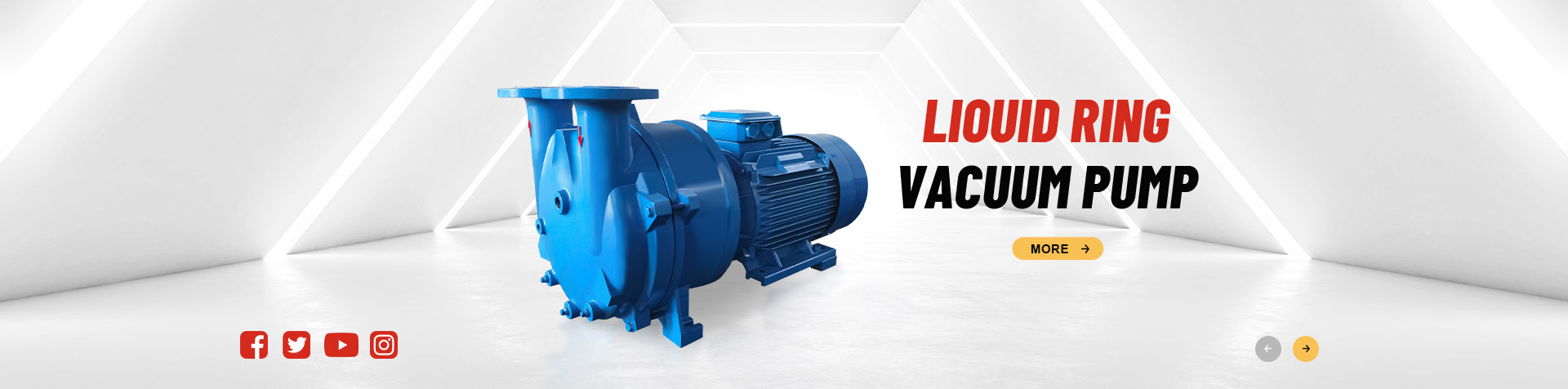


-
What are the reasons why claw vacuum pumps cannot pump water?
2025-08-21
When using a vacuum pump, you may encounter a problem where it cannot draw water. Why does this happen? Based on years of experience, vacuum pump manufacturers have summarized the following reasons for this issue.
-
What are the requirements for the oil used in oil-sealed rotary vane vacuum pumps?
2025-08-12
1. Extremely low vapor pressure; 2. Appropriate viscosity and good viscosity-temperature characteristics; 3. Good thermal and oxidative stability; 4. Good corrosion resistance and anti-emulsification properties; 5. High flash point.
-
What causes cavitation in water ring vacuum pumps?
2025-08-03
The critical pressure at which cavitation occurs varies depending on the properties of the liquid, temperature, and properties of the dissolved gas. According to information on water pumps, for degassed water at normal temperature, the saturated vapor pressure at that water temperature can be used as the critical pressure value at which bubbles occur.
-
What is the exhaust pressure of an oil-free rotary vane vacuum pump?
2025-07-31
Exhaust pressure has a significant impact on the intake volume and shaft power consumption of a vacuum pump. When a vacuum pump system is in operation, the greater the exhaust pressure, the smaller the intake volume of the vacuum pump, and correspondingly, the greater the shaft power consumption.
-
Vacuum pump parts need to be thoroughly cleaned
2025-07-23
During the maintenance of vacuum pumps, if oil-free vacuum pump manufacturers fail to pay attention to strengthening the cleaning of impurities on the surface of components, or if the cleaning methods are improper, it will lead to wear and corrosion damage to the components, thereby seriously affecting the maintenance quality and service life of the vacuum pump after maintenance.
-
How to extend the service life of water ring vacuum pumps
2025-07-18
To extend the service life of water ring vacuum pumps, comprehensive measures should be taken in five areas: design selection, installation environment, operating procedures, maintenance and servicing, and fault prevention.
Address:
No. 1-1-2203, VANKECHENG DONGYUAN HONGJIA ST, JIAOJIANG TAIZHOU ZHEJIANG, CHINA
Tel:
+86-13858665170
E_mail:
sales@yizhivac.com


PRODUCTS
CONTACT US